 Conjugation
Conjugation
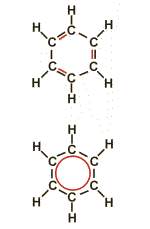
Double bonds, separated by only one single bond (formula above), are called "conjugated".
The chemical formulas for representing covalent bonds are based on the simplified assumption that the electrons of a given bond can be treated isolated from the other electrons of the molecule. In the case of conjugated double bonds, this simplification is no longer possible. Such bonds are better described by a model combining the electrons of all conjugated bonds and distributing them over the participating carbon atoms (formula below). This phenomenon is called mesomery. A special group of compounds characterized by mesomery are aromates.