 Ketones
Ketones
Compounds containing an oxygen atom connected to a carbon atom via a double bond are either ketones or aldehydes. In the case of ketones, the respective carbon atom is bound to two other carbon atoms (and not to a hydrogen atom as in the case of aldehydes).
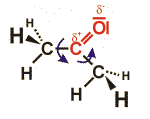
The graphical example shows the structural formula of a ketone consisting of three carbon atoms (acetone). Due to the influence of the oxygen atom, the central carbon atom is partially charged positively – it easily reacts with other groups. Due to the double bond, the oxygen atom and the three carbon atoms are lying within one common plain. The covalent bonds between the carbon atoms can rotate freely. Accordingly, there are many possible structures; the structure shown gives only one of these possibilities.
Ketones, similar as aldehydes, can be produced by the oxidation of respective alcoholes. In contrast to aldehydes, however, they cannot be further oxidized to carbonic acids.