 Amides
Amides
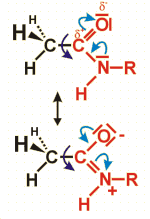
Amides are formed by condensing acids and amines (resulting in the liberation of one molecule water).
The figure gives the structural formula of an amide composed of acetic acid and an unspecified amine (with the unknown residue R). Due to the two mesomeric formulas presented, both bonds connecting the carbon with the oxygen and the nitrogen atom are partially double bonds. Therefore, the group marked in red together with the second carbon atom of the acid lie within one common plain.