 Peptide bonds
Peptide bonds
Connection of amino acids in protein chains.
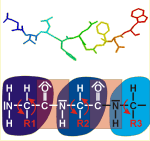
Proteins consist of amino acids connected by their amino and carbonic acid groups in the form of amides. As a result, the backbone of proteins is constituted of repetitive, identical units, while the variable side chains of the amino acids are extending away from the backbone.
The model presented depicts a protein chain made of ten amino acids; the structural formula is given for the first three amino acids. Different amino acids are marked by different colours, The different side chains are designated R1, R2, and R3.
The peptide bond is – like any amide – fixed in a planar arrangement, due to mesomeric effects (marked in pink). The other bonds of the protein chain, in contrast, can rotate freely (red arrows) resulting in the high sterical flexibility of protein chains. The exact folding of proteins is crucial for their biological function.