 Amino acids
Amino acids
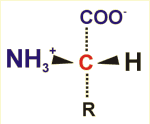
Organic compounds containing one or more carboxy- (COO-) and one or more amino groups (NH2).
Proteins are composed of twenty different amino acids, which are differing from each other by the variable residue R. These amino acids are chiral compounds, because four different groups are attached to the central carbon atom (red). Only the form shown here, not its mirror image, is used for protein biosynthesis.