 Catalysts
Catalysts
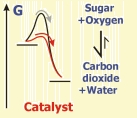
Catalysts reduce the activation energy of a given reaction and this way shorten the time necessary for reaching the chemical equilibrium.
The reaction of sugar with oxygen (the "burning" of sugar) is leading to carbon dioxide and water. Although the equilibrium of this reaction lies far on the side of the products, sugar is not reacting under normal conditions, due to the large activation energy. The reaction only works after investing this energy, or after using catalysts reducing the activation energy.