 Gibbs Free Energy (G)
Gibbs Free Energy (G)
Gibbs Free Energy refers to the order of a given system and determines the concentrations of reactants and products of a given chemical reaction in the state of chemical equilibrium.
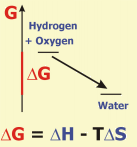
The example shows the reaction of hydrogen and oxygen to water. Gibbs Free Energy for this reaction is calculated from the thermal disorder (the amount of energy (enthalpy, H) liberated in the reaction) and from the molecular disorder (entropy S) by the formula given above. In the case of hydrogen and oxygen, the increase in thermal disorder (due to the large amount of energy liberated) largely outweighs the small decrease in molecular disorder (due to the decrease of the number of molecules). Accordingly, Gibbs Free Energy is negative, the chemical equilibrium is characterized by high concentrations of the product and low concentrations of reactants.