 Entropy (S)
Entropy (S)
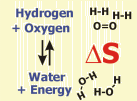
According to the second law of thermodynamics, all processes increasing disorder are occuring spontaneously. Entropy (S) refers to the molecular disorder of a given reaction, enthalpy (H) refers to the respective thermal disorder. The combination of both factors results in Gibbs Free Energy.
The example gives the reaction of hydrogen and oxygen to water. Entropy (the molecular disorder) is decreasing in this reaction, because the number of molecules is decreasing. Because the reaction of hydrogen and oxygen liberates a large amount of energy, however, thermal disorder is largely increased and the reaction can proceed spontaneously.