 Roots
Roots
Basal organ of vascular plants involved in the anchoring of plants in the soil and in the uptake of water and mineral nutrients (phosphate, nitrate, ammonia, potassium...).
Typical root systems of dicotyledons are formed by one main root with several branching lateral roots (as depicted here). Root systems of pteridophytes and monocotyledons, in contrast, are formed by a number of parallel similarly formed lateral roots (without a main root).
Roots are growing at their tips. Their
vascular bundles are arranged together in the
central cylinder,
while the tissues for the uptake of water and nutrients
are forming the outer layers of the root
(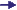 structural plan).
Many plants use roots as storage organs (beets,
root tubers) in particular for
starch.
structural plan).
Many plants use roots as storage organs (beets,
root tubers) in particular for
starch.