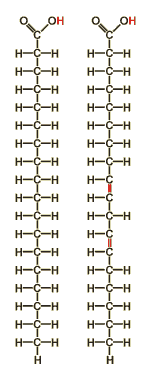
 Fatty acids
Fatty acids
Long chain carbonic acids characterized by a large energy content and by amphiphilic properties.
Fatty acids are highly reduced organic compounds containing only few oxygen atoms. This highly reduced nature is responsible for the high energy content. The amphiphilic properties are due to the uneven distribution of oxygen atoms: The carbonic acid group is hydrophilic, the long hydrocarbon residue is hydrophobic. Because of their amphiphilic properties, fatty acids can be used as detergents (soaps). In living organisms, most fatty acids are integrated in lipids.
Fatty acids which canīt be produced by the human body and have to be taken up by food, are called essential fatty acids. Most of these compounds are containing double bonds (marked in red colour on the right side of the figure).