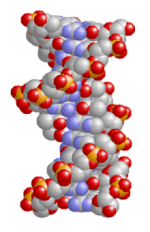
 DNA
DNA
Deoxyribonucleic acid; Long, chain-like molecules, containing the heritable information (the sequence) for the construction of proteins.
The model displays the DNA double helix composed of two molecular strands wound (in different directions) around a common axis. Phosphorus atoms (yellow) and oxygen atoms (red) are marking the backbone of the two single strands (formed by alternating phosphate- and deoxyribose residues). The bases (marked by the blue nitrogen atoms) are connected to the deoxyribose residues and are extending into the internal space of the helix. There, they are binding their appropriate counterparts by specific hydrogen bonds.