 Base pairing
Base pairing
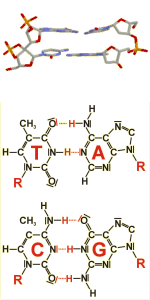
Due to the formation of specific hydrogen bonds, the bases adenine (A) and thymine (T)/uracil(U) on the one hand and guanine (G) and cytosine (C) on the other are always situated opposite to each other in DNA or RNA double strands.
The upper part of the figure shows two consecutive building blocks (nucleotides) of such a DNA double strand. The pairing bases are marked in blue colour. The lower part of the figure displays the two possible base pairings. The hydrogen bonds are marked in red colour.
Base pairing is responsible for the aggregation of DNA-, or RNA- single strands into double strands. This formation of double strands is essential for DNA-replication and transcription.