 cDNA
cDNA
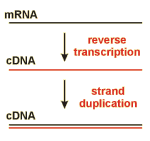
Complementary DNA; DNA-molecules, formed by copying the sequence of mRNA-molecules.
The mRNA-molecules of a given cell or a group of cells refer to the genetic information, which is used by these cells. This information can be analyzed more easily in the form of DNA in comparison to RNA. Copying of RNA sequences into DNA (reverse transcription) is a rare process in nature. Some viruses, however, which are storing their genetic information in the form of RNA, possess respective enzymes. These enzymes can be used for copying the sequence of mRNA in the laboratory. (In a second step, the newly formed single stranded DNA-molecules are duplicated resulting in double stranded molecules.)
The production of cDNA is the starting point for a number of analytic methods: Individual sequences can be multiplied by PCR and examined in detail, the complete number of all sequences copied can be cloned and multiplied using bacteria. Short, randomly selected parts of cDNA sequences are called EST-sequences.