 Core of the earth
Core of the earth
Inner part of the earth consisting of particular dense material (iron, nickel).
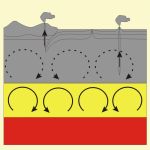
The core of the earth consists of an internal solid part (red colour) and an external fluid part (yellow colour). During transition of material from the external to the internal part, large amounts of energy are liberated. This energy together with energy liberated by natural radioactive isotopes is responsible for heating up the internal of the earth. The temperature at the border between inner and outer core (5000 kilometres below ground) goes up to 4600 degrees celsius, the pressure to 3000 bar.
Thermal differences between the core and the mantle are resulting in rapid convection currents within the outer core (arrows). These currents are responsible for the magnetic field of the earth.