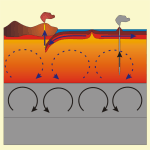
 Continental drift
Continental drift
Dislocation of continental plates against each other.
Fuelled by the thermal differences between the interior of the earth and the earth surface, the inner, viscous part of the mantle is subjected to slow convection currents (dotted arrows). The continental plates are torn apart or pushed against each other by these currents. The collision of continental plates results in the formation of deep-sea trenches – one of the plates is torn below the other. The separation of continental plates occurs in general under the sea at oceanic ridges, where updwelling, hot material is forming new sea-floor.