 Cell division
Cell division
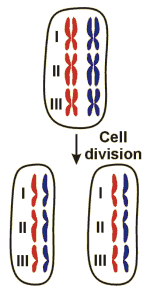
Division of a cell into two daughter cells.
The figure shows the division of a cell, which contains the double set of chromosomes (diploid) consisting of three different chromosomes (I, II, and III). The different colours mark the origin of the chromosomes from the two different parents of the organism in question. The respective DNA molecules have been duplicated prior to cell division, resulting in the presence of two identical DNA molecules per chromosome. During cell division each of these identical molecules is distributed to one of the daughter cells. Prior to the next cell division, the DNA molecules have to be duplicated again.