 Sexual reproduction
Sexual reproduction
Mode of reproduction resulting in the mixing of genomes of two organisms prior to the formation of the new generation.
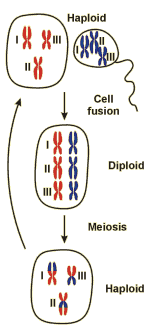
Two germ cells, each containing one complete set of chromosomes (haploid; I, II, III in this example) are fused in the course of sexual reproduction . The resulting cell contains a double set (diploid) of chromosomes. In most cases, this cell is forming the adult organism by cell division, without a reduction of the chromosome set. Prior to the production of new germ cells, however, this double set has to be reduced in a process called meiosis. During meiosis, the chromosoms stemming from the two parent organisms marked in different colours are mixed and corresponding pieces of the chromosomes are exchanged against each other, resulting in a mix-up of parental genes.