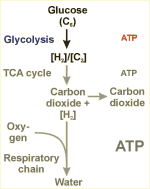
 Glycolysis
Glycolysis
Reactions leading to the disintegration of glucose into smaller units ([C2, carbon dioxide) liberating a certain amount of energy (ATP) and reduction equivalents ([H2]).
A part of the energy liberated during glycolysis is conserved in the form of ATP. The reduction equivalents produced are oxidized in most cases by the respiratory chain, leading again to the production of ATP. In the absence of oxygen, however, the reduction equivalents have to be transferred to the products of glycolysis (fermentation). Depending on the respective products, these pathways are called alcoholic fermentation, lactic acid fermentation or acetic acid fermentation.