 Active transport
Active transport
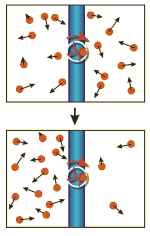
Transport of a given compound resulting in the accumulation of this compound on one side of a biological membrane.
Cell membranes prevent the diffusion of most compounds. Specific membrane proteins, however, are able to facilitate the passage of specific compounds. The action of such proteins can result in the equilibration of concentrations (passive transport, the proteins are acting for example as channels), or in the formation of such differences (active transport). Active transport has to be fuelled by chemical energy, e.g. in the form of ATP.