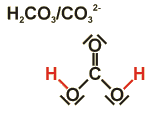
 Carbonic acid/ Carbonate
Carbonic acid/ Carbonate
Carbonic acid can liberate two protons. The acid is formed by reactions of carbon dioxide and water. The twofold negatively charged ion of carbonic acid is named carbonate, respective salts carbonates. (For example soda ash (sodium carbonate), potash (potassium carbonate) or limestone (calcium carbonate)).