 Antibodies
Antibodies
Proteins binding specific structures and marking them as "foreign".
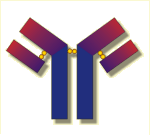
Antibodies are large complexes composed of several protein chains (see figure). They are binding their target structures at the sites marked in red colour. Early in the development of a given organism, antibodies specific for structures of the organism itself are eliminated. Structures recognized later are "foreign" and are attacked after recognition by the respective antibody. Vertebrates in particular are using this strategy to defend themselves against pathogens.
Antibodies, which have once been used successfully against foreign structures, can be easily mobilized in the case of a later contact. This way, organisms achieve immunity against the respective pathogens.